Lead exposure is responsible for a range of human health impacts, with even relatively low levels impacting the cognitive development of children. DRI scientists have previously used atmospheric pollution records preserved in Arctic ice cores to identify periods of lead pollution throughout the Roman Empire, and now new research expands on this finding to identify how this pollution may have affected the European population.
Frequent Disturbances Increased the Resilience of Past Human Populations
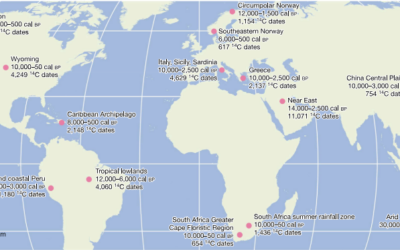
DRI’s Erick Robinson, Ph.D., associate research professor of climate and archaeology, is co-author on a ground-breaking new study. The research, published May 1st in Nature, is the first global-scale comparison of human resilience to environmental and cultural disturbances over millennia.
Ancient Pollen Trapped in Greenland Ice Uncovers Changes in Canadian Forests Over 800 Years
The new study helps illuminate how changes in forest composition followed European settlement and natural changes in climate.
The First Assessment of Toxic Heavy Metal Pollution in the Southern Hemisphere Over the Last 2,000 Years
An international team of scientists led by DRI found evidence of Southern Hemisphere heavy metal pollution preserved in Antarctic ice cores from early Andean cultures and Spanish Colonial mining that predates the Industrial Revolution by centuries.